Thermo-fluid-science field laboratories
Fluid engineering
Staffs
- Masahide NAKAMURA (Professor, Dr. Eng.)
- Orie TAMURA (Technical Staff)
Research interests
Fluid mechanics, especially numerical fluid mechanics and its application to the fluid machinery. As for the numerical fluid mechanics, our attentions are paid to the flow with the moving boundary. This analysis has a strong relation with the flow near the moving insect or the reduction of the flow resistance. Moreover, the study on the microbubble is carried out with the intention of purifying water quality. Various applications are expected for this research.
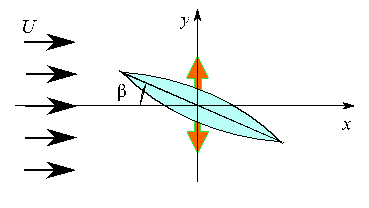
To understand the mechanism of the insect flying, we calculated the flow near the oscillating wing (see Fig.1).
In this model, the angle of attack was kept constant. The calculated efficiency of the thrust force is shown in Fig.2. In this figure, St is the non-dimensional oscillating frequency and type A has large thickness compared with type B. This figure shows that the wing geometry has the strong effect on the efficiency.
| Research themes |
|---|
|
Heat transfer engineering
Staffs
- Makoto TAGO (Professor, Dr. Eng.)
- Hirotake AKATA (Technical Staff)
Research interests
Heat and mass transfer, including a geothermal energy extraction and melting behavior in binary aqueous solution.
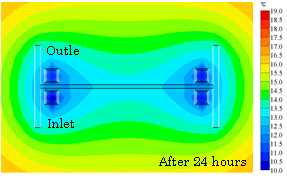
Fig.1 Temperature distribution around U-tube downhole heat exchanger
Several Types of downhole heat exchangers, for example downhole coaxial heat exchanger, U-tube downhole heat exchanger, have been proposed in order to extract heat directly from shallow geothermal resources. A U-tube downhole heat exchanger is widely used, not only in Japan but also around the world, because of its advantages of cost performance and ease of construction.
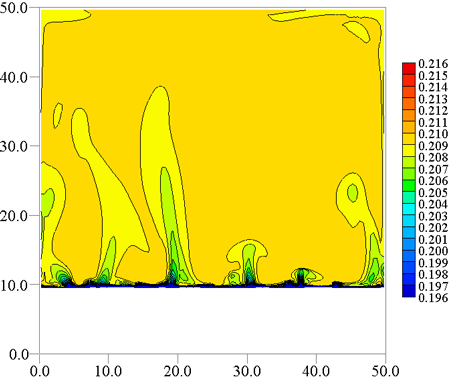
Fig.2 Concentration distribution in binary aqueous solution on ice
The ice when melting with a chloride aqueous solution is accompanied by mass transfer, freezing point depression, and the absorption of the latent heat of fusion. Therefore, double diffusive convection of temperature and concentration occurs in an aqueous solution, and melting behavior of the ice layer becomes very complicated.
| Research themes |
|---|
|
Heat transfer engineering
Staff
- Yoshimi KOMATSU (Associate Professor, Dr. Eng.)
Research interests
Heat and mass transfer, especially phase change phenomena in environmental and engineering fields for examination of melting of ice into seawater, thermal latent heat storage devices, and the melting of snow on roads. Freeze proofing techniques related to a drainpipe resulting from melted snow on a roof in cold districts.
Freezing begins because of droplets remaining by surface tension effects in each point at the lower end, and icicles are formed at various locations. Droplets come to remain in gaps of each icicle. Therefore, the surface area of icicles increases, thereby promoting further icicle growth. Finally, the lower end becomes completely frozen, engendering pipe blockage. We controlled the water flow by developed drainpipe. Results show that branching was reduced and flow velocity was increased. Droplets remaining on the surface of the lower end were therefore reduced, thereby suppressing freezing.
| Research themes |
|---|
|
Fluid engineering
Staff
- Wataru SUGIYAMA (Lecturer, Dr. Eng.)
Research interests
Small wind turbine
Small wind turbines are often worked at unsteady wind environment. At low wind speed environment, there are very low energy levels. It is important to improve the efficiency of a wind turbine.
Rarefied gas flow
Rarefied gas flows in narrow spaces are affected by the interaction between gas molecules and walls of passages.
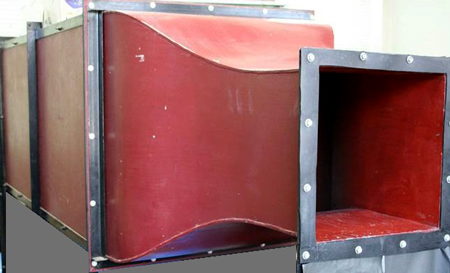
Fig.1 Wind tunnel
The wind tunnel makes uniform flow field at the outlet of the tunnel (the right side of the figure 1). Wind turbine models tested in the flow field.
Fig. 2 Vacuum chamber
The vacuum chamber is made of stainless steel. The gas in the vacuum chamber is evacuated by vacuum pumps. A passage is set in the vacuum chamber, and then rarefied gas flow in the passage is tested.
| Research themes |
|---|
|